Solid-state terahertz devices could scan for cancer
By Bill Steele

Cornell researchers have developed a new method of generating terahertz signals on an inexpensive silicon chip, offering possible applications in medical imaging, security scanning and wireless data transfer.
Terahertz radiation, the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum between microwaves and infrared light, penetrates cloth and leather and just a few millimeters into the skin, but without the potentially damaging effects of X-rays. Terahertz scanning can identify skin cancers too small to see with the naked eye. Many of the complex organic chemicals used in explosives absorb terahertz radiation at particular frequencies, creating a "signature" that detectors can read. And because higher frequencies can carry more bandwidth, terahertz signals could make a sort of super-Bluetooth that could transfer an entire high-definition movie wirelessly in a few seconds.
Current methods of generating terahertz radiation involve lasers, vacuum tubes and special circuits cooled near absolute zero, often in room-sized apparatus costing thousands of dollars. Ehsan Afshari, assistant professor of electrical and computer engineering, has developed a new method using the familiar and inexpensive CMOS chip technology, generating power levels high enough for some medical applications. With further research, higher power will be possible, Afshari said, enabling such devices as handheld scanners for law enforcement.
Afshari and graduate students Yahya Tousi and Vahnood Pourahmad describe the new approach in the June 8 issue of the journal Physical Review Letters.
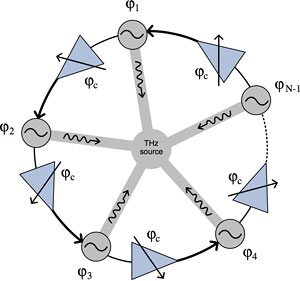
The ability of solid-state devices to generate high frequencies is limited by the characteristics of the material -- basically, how fast electrons can move back and forth in a transistor. So circuit designers make use of harmonics -- signals that naturally appear at multiples of the fundamental frequency of an oscillator. That fundamental frequency is usually set by a circuit that uses a variable capacitor called a varactor, but at terahertz frequencies varactors don't tune sharply. Afshari has come up with a new way of tuning by coupling several oscillators in a ring, producing what engineers call a high-quality signal, where all the power goes into a very narrow frequency band.
Connect two springs and set one vibrating, and the other will begin to vibrate as well, and eventually they will settle to an equilibrium. A ring of electronic oscillators does the same, and the circuits coupling the oscillators can set the frequency at which they will lock in. In Afshari's device the couplers also shift the phase of the signals, that is, how the peaks and valleys of the waves line up. With the right adjustment, the peaks and valleys cancel each other out at several harmonics but reinforce each other at one -- in this case the fourth -- channeling most of the power there.
In early experiments, the researchers fabricated chips that generated signals with about 10,000 times the power level previously obtained at terahertz frequencies on a silicon chip. The signal emerges along the axis of the ring, and what the researchers called an intriguing possibility is that by adjusting the couplers separately they could aim the output, making it possible to scan large areas with a narrow, high-powered beam.
The power could be increased by adding more oscillators to the ring or using multiple rings, and Afshari is working with Cornell experts on gallium nitride, a chip material that can handle both higher frequencies and higher power. But Afshari said he wants to focus on less-expensive silicon. "The goal is to make a complete device on one CMOS chip," he said. "I can envision a tiny thing you could put in a cell phone."
The research is funded by the National Science Foundation, the U.S. Office of Naval Research and the Semiconductor Research Corp., a consortium supported by private industry and the Defense Advanced Projects Research Agency.
Media Contact
Get Cornell news delivered right to your inbox.
Subscribe